In a terrifying incident in Rawalpindi, a swarm of honey bees attacked around 80 schoolchildren, causing widespread panic and sending several of the children to the hospital. The students, who were engaged in their usual school activities, found themselves swarmed by bees in what became a chaotic and life-threatening situation.
The incident has sparked concerns about safety measures in educational institutions and raised questions about the increasing number of such attacks in populated areas. It also brings attention to the behavior of honey bees and the growing risks posed by human encroachment on natural habitats. While bees play a critical role in maintaining ecosystems, interactions between humans and these creatures can sometimes result in dangerous situations, especially when bees feel threatened or disturbed.
This article aims to explore the Rawalpindi bee attack, its causes, the reactions to it, and the broader context of bee-related incidents, including the role of honey bees in ecosystems and what can be done to mitigate future risks.
The Incident: Chaos in the Schoolyard
The attack took place in a school in Rawalpindi, where 80 children were suddenly swarmed by a large number of honey bees. According to witnesses, the bees appeared out of nowhere, and within moments, the school turned into a scene of panic. Teachers and students ran for cover as the bees stung the children indiscriminately, causing distress, pain, and swelling.
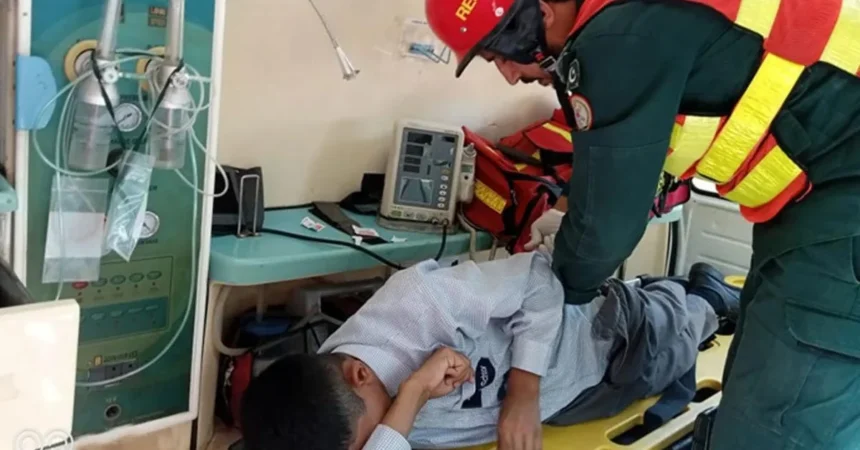
Many of the children were stung multiple times and had to be rushed to nearby hospitals for immediate medical treatment. Fortunately, there were no fatalities, but several students required urgent medical care due to allergic reactions and the severity of their stings.
Immediate Response and Medical Attention
Following the attack, teachers and school staff quickly moved to get the children indoors, away from the bees. Emergency services were called in, and the affected students were transported to hospitals. Doctors reported treating multiple cases of bee stings, with some children suffering from serious allergic reactions known as anaphylaxis, which can be life-threatening without prompt treatment.
Several students were kept under observation to ensure that they did not suffer any delayed allergic reactions. The attack left the school community shaken, and many parents expressed concerns about the safety of their children in school premises, particularly in outdoor areas.
Understanding Honey Bee Behavior
While honey bees are not typically aggressive, they can become defensive and attack when they feel their hive or queen is threatened. This swarm behavior is part of a protective instinct ingrained in bees to defend their colony from perceived threats. However, when bees are disturbed in large numbers or become agitated, they can attack en masse, stinging repeatedly to protect their hive.
Why Do Bees Attack?
Bee attacks are not random; they are a defense mechanism. When bees sense danger to their hive or feel disturbed, they release pheromones that signal other bees to come and defend their territory. This triggers a swarm attack, where hundreds or even thousands of bees may target the perceived threat.
In the case of the Rawalpindi attack, it is unclear what exactly triggered the bees, but it’s likely that their hive was located nearby, and something disturbed them, prompting the swarm to attack the children. Construction work, loud noises, or even rapid movements can trigger this defensive response.
Another factor to consider is the time of year. Bees tend to be more aggressive during certain seasons, particularly when they are foraging or storing food. It’s possible that the bees in this case were more sensitive to disturbances due to the natural cycle of their hive activity.
Human Encroachment and Bee Habitats
Incidents like the one in Rawalpindi bring to light the growing issue of human encroachment on natural bee habitats. As urban areas expand and natural environments shrink, bees are increasingly coming into contact with human populations. This proximity often leads to unintended encounters, such as the one seen in this case, where bees may feel threatened by human activities, leading to defensive swarming.
Urban Expansion and Natural Habitats
Rapid urbanization is a major contributor to the increasing number of human-bee encounters. In areas where forests, fields, or even gardens once thrived, residential and commercial developments have now taken over, leaving bees with fewer places to nest. As bee populations struggle to find habitats, they sometimes settle near schools, homes, or public areas, increasing the likelihood of interaction with people.
Honey bees, in particular, are known to build hives in unexpected locations, such as hollow trees, wall cavities, or under eaves. In densely populated areas, this can be dangerous, as people may unknowingly disturb these hives, leading to aggressive behavior from the bees.
Protecting Bee Populations Without Compromising Human Safety
While bees are vital for pollination and play a crucial role in food production and biodiversity, it’s essential to balance the need to protect these insects with the safety of human populations. Education on bee behavior, as well as precautionary measures, can go a long way in reducing the chances of harmful encounters.
Preventing Future Bee Attacks: Safety Measures for Schools and Public Spaces
In the aftermath of the Rawalpindi incident, there has been a strong call for better safety measures in schools and other public spaces to prevent future bee attacks. While bee stings are usually manageable, mass stings, especially among children, can lead to severe reactions and medical emergencies.
Hive Removal and Relocation
One of the most important steps schools and local governments can take is to monitor for bee activity on school grounds and in nearby areas. If a hive is found, it should be professionally removed and relocated to a safer area. Pest control services trained in handling bees can safely relocate hives without harming the bees, allowing them to continue their essential role in the ecosystem while reducing the risk of attacks on humans.
In many cases, bee relocation can be coordinated with local beekeepers or environmental agencies that are experienced in handling bee populations. This ensures that the bees are moved to a more suitable habitat where they are less likely to come into contact with humans.
School Safety Protocols
Schools can also establish protocols for bee safety, ensuring that students and staff know what to do in the event of a bee swarm. This includes creating awareness about bee behavior and ensuring that students are trained to avoid sudden movements or loud noises if bees are present.
In addition, schools should consider installing bee traps or deterrents in areas where children play or spend time outdoors. These traps can help prevent bees from nesting in close proximity to school buildings, reducing the likelihood of an incident like the one in Rawalpindi.
Emergency Medical Preparedness
Given the risk of allergic reactions to bee stings, schools should be prepared to deal with medical emergencies. This includes keeping antihistamines and epinephrine auto-injectors (EpiPens) on hand to treat severe allergic reactions like anaphylaxis. School staff should also be trained in recognizing the signs of an allergic reaction and administering first aid.In the case of a mass sting incident, having a well-coordinated emergency response plan can help ensure that children receive prompt medical attention, minimizing the risks associated with bee stings.
The Role of Honey Bees in the Ecosystem
It’s important to remember that while incidents like the Rawalpindi attack are alarming, honey bees are essential to the health of our planet. Bees are among the most important pollinators in the world, responsible for pollinating approximately one-third of the food we eat. Without bees, crops such as fruits, vegetables, and nuts would struggle to grow, leading to significant food shortages and economic challenges.
Pollination and Food Security
Honey bees play a crucial role in pollinating crops that are vital for human consumption, including apples, almonds, blueberries, and cucumbers. Their work supports the growth of food that not only sustains human populations but also feeds livestock. Bees also contribute to the pollination of wild plants, which helps maintain biodiversity and the health of ecosystems.
In recent years, there has been growing concern about the decline in global bee populations due to factors such as habitat loss, pesticide use, and climate change. Protecting bees is essential for maintaining food security and ecosystem stability, but this must be done in a way that prioritizes human safety.
The Balance Between Conservation and Safety
As we strive to protect honey bees and other pollinators, it’s important to find a balance between conservation efforts and public safety. Incidents like the one in Rawalpindi serve as a reminder that bees, while crucial for the environment, can pose risks when their habitats overlap with human activity.
Raising Awareness and Preventing Panic
One of the key lessons from the Rawalpindi attack is the importance of public awareness about bee behavior and safety. When people understand why bees attack and how to avoid disturbing them, the risk of future incidents can be significantly reduced.
Educational campaigns in schools, public spaces, and communities can help people recognize the signs of bee activity and take appropriate precautions. For example, avoiding the use of strong-smelling perfumes, keeping food covered outdoors, and not swatting at bees are all simple ways to reduce the likelihood of an encounter turning dangerous.
#RawalpindiBeeAttack #BeeSafety #HoneyBeeSwarm #BeeConservation #PublicSafety #SchoolSafety #Beekeeping #EnvironmentalAwareness #BeePopulation #PollinatorProtection #HumanWildlifeConflict #AllergicReactions #BeeSwarm