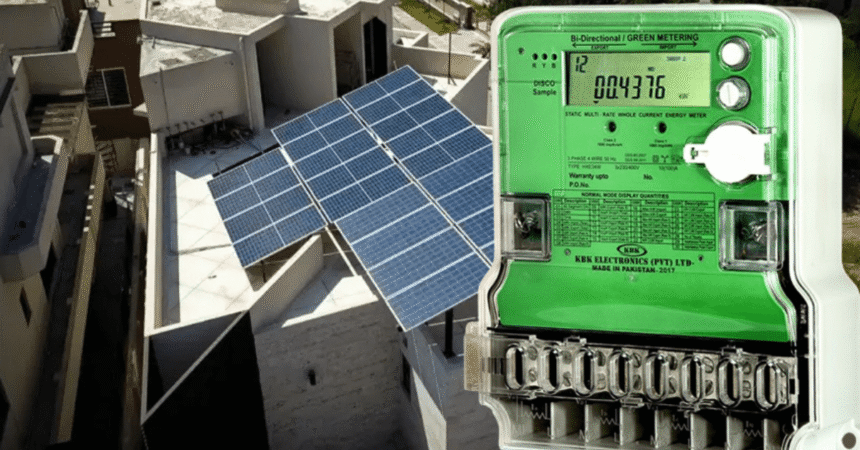
As electricity costs in Pakistan continue to escalate, a significant transformation is underway in the energy consumption patterns of its citizens. The move towards alternative energy sources, particularly solar power, has gained remarkable momentum in recent years. This trend reflects not only a response to rising electricity tariffs but also a growing awareness of the benefits of renewable energy.
The Rising Costs of Electricity
Pakistan has been grappling with increasing electricity tariffs, compounded by fixed charges that have put a strain on household and commercial budgets. The situation has led many to seek more sustainable and cost-effective alternatives to traditional energy sources. The government’s efforts to manage the energy crisis have often fallen short, leaving consumers with few options but to look outside the national grid.
The rising costs can be attributed to several factors, including inefficiencies within the energy sector, reliance on imported fuels, and the financial burdens of maintaining the national grid. As a result, many citizens are exploring net metering as a viable solution, allowing them to generate their own electricity and reduce dependence on conventional power supplies.
Net Metering: A Popular Alternative
Net metering has emerged as one of the most favored alternatives for electricity consumers in Pakistan. This system allows individuals and businesses to generate their own solar power and feed any excess energy back into the national grid, receiving credits in return. Over the past year, the number of net metering users in Pakistan has skyrocketed from 60,000 to 200,000, effectively doubling its contribution to the country’s energy mix.
The capacity associated with net metering has also seen a dramatic increase, rising from 1,500 MW to 3,000 MW. This surge reflects a growing recognition of the economic and environmental benefits of solar energy. The proliferation of solar installations has been driven by a combination of decreasing costs for solar technology, government incentives, and rising public awareness regarding climate change and energy independence.
Impact on National Grid Consumption
The shift towards net metering has resulted in a notable 12% annual reduction in overall electricity consumption from the national grid. As more households and businesses adopt solar energy, the demand on the grid has decreased, creating a dual effect: it alleviates some pressure from the overloaded system while also challenging the sustainability of the grid itself.
With fewer consumers relying on the traditional grid, the remaining users face the burden of maintaining the infrastructure. This shift raises questions about equity and sustainability within the energy system. Consumers still dependent on the national grid may experience higher costs as the financial load increasingly shifts onto them.
The Solar Panel Market
Currently, Pakistan boasts between 6,000 to 7,000 MW of imported solar panels. This figure underscores the rapid growth of the solar energy sector, which has been supported by various local and international investments. The competitive pricing of solar technology, coupled with government incentives, has made it an attractive option for many households and businesses.
However, the influx of solar panels and systems has raised concerns regarding the sustainability of the energy market. As the number of net metering users grows, the government must address the implications for the national grid and the energy contracts that underpin it.
Challenges for the National Grid
The shift to solar energy poses several challenges for the national grid. As more people opt for net metering, the burden of maintaining the grid increasingly falls on a smaller group of consumers. This situation raises significant sustainability concerns, as the financial viability of the grid becomes questionable when a substantial portion of users generates their own power.
The government is now under pressure to reevaluate its agreements with independent power producers (IPPs). These contracts often lock the government into fixed pricing structures that may no longer align with the realities of a transitioning energy market. Adjusting these agreements could be critical for ensuring the stability of the power supply while addressing the financial challenges posed by the increasing shift toward renewable energy.
Economic and Employment Opportunities
The growth of the solar energy sector in Pakistan has not only been a response to rising electricity costs but has also created new economic opportunities. The solar market has led to job creation in various fields, including manufacturing, installation, and maintenance of solar systems. This job creation is vital for the economy, especially in a country where unemployment rates remain a concern.
Furthermore, as the market for solar technology expands, a diverse range of companies and entrepreneurs are entering the space, providing various solutions and services. This has led to increased competition, which can further drive down costs for consumers and make solar energy more accessible.
Consumer Education and Market Complexity
Despite the growth of the solar market, many consumers face challenges when navigating their options. Limited knowledge about solar technology can lead to confusion and hesitation among potential adopters. Many citizens may not fully understand how net metering works, the benefits of solar energy, or the various pricing options available.
This complexity necessitates increased consumer education and outreach. Various organizations, including non-profits and government bodies, must work together to inform the public about the benefits of solar energy and how to navigate the installation process effectively. By providing clear information, consumers can make informed choices that best suit their energy needs.
The Role of Government Policies
Government policies play a crucial role in shaping the solar energy landscape in Pakistan. Supportive policies can encourage the adoption of renewable energy, while regulatory frameworks must adapt to the evolving energy market. The government has implemented several initiatives aimed at promoting solar energy, including subsidies, tax incentives, and net metering regulations.
However, these policies must be continuously assessed and revised to ensure they meet the needs of a changing energy landscape. As net metering becomes more prevalent, the government will need to create a regulatory framework that balances the interests of solar users with the sustainability of the national grid.
The Future of Solar Energy in Pakistan
The future of solar energy in Pakistan appears promising, with the potential for continued growth and innovation. As technology advances and costs decrease, more individuals and businesses are likely to adopt solar energy solutions. This transition will contribute to a more sustainable energy future and help mitigate the challenges posed by climate change.
Moreover, as awareness about the benefits of solar energy continues to grow, the market will likely see further diversification in products and services. New players may emerge, offering innovative solutions that cater to the unique needs of Pakistani consumers.
In summary, the shift towards solar energy and net metering in Pakistan reflects a broader trend of seeking sustainable and cost-effective energy solutions. While this transition presents challenges for the national grid, it also opens up new economic opportunities and avenues for innovation. By addressing the complexities of the solar market and enhancing consumer education, Pakistan can ensure a more sustainable energy future that benefits all its citizens.
#SolarEnergy #NetMetering #Pakistan #RenewableEnergy #ElectricityCosts #Sustainability #CleanEnergy #SolarPower #EnergyTransition